EstroMetab (30 capsules) by Compounded Nutrients
About this product
Recommended Uses:
Helps support estrogen metabolism and balance in both women and men.
Recommended Dosages:
1 capsule, 2 times daily.
Product Overview:
Estrogen is thought of as a hormone that is involved in female reproduction, but it also occurs in males in smaller amounts and affects the growth, differentiation and function of many tissues in the body. Estrogen is a term that is used to collectively describe the hormones estradiol, estrone and estriol. In the body, estrogens circulate mainly bound to the sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and only unbound (or “free”) estrogens can enter cells and lead to biological effects.1 Various lifestyle and environmental factors can influence the production, binding, metabolism and function of estrogen in men and women, including:
Genetics
Age
Poor diet, high in refined carbohydrates like white breads, sugars and low in vegetables, low fiber and high saturated fat
Excessive alcohol consumption
Poor glycemic control and insulin signaling sensitivity
Certain medications, including hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and oral contraceptives (OC’s)
Exposure to environmental contaminants (xenoestrogens) such as pesticides, found in industrial chemicals and foods contaminated with agricultural hormones
Excessive visceral fat
The major method that estrogen affects the body depends on its metabolism. The metabolism of estrogen takes place mainly in the liver through Phase I (hydroxylation) and Phase II (methylation and glucuronidation) pathways, allowing estrogen to be detoxified and excreted from the body. Estrogen is also metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract, and is dependent upon cofactors including the microflora, vitamin B6, B12 and folic acid. Approximately 50% of estrogen conjugates produced in the liver are excreted into the bile and pass into the intestines, where they can become hydrolyzed by the intestinal bacterial enzyme beta-glucuronidase, and are either excreted fecally or reabsorbed.
As women age, their estradiol levels goes down and their estrone levels increase and in men their relative estradiol and estrone levels go up. Both men and women will make more estrogens if they accumulate visceral (belly) fat. Excessive estrogen stimulates tissue growth and can affect the ovaries and breast in women and the prostate tissue in men. Estrone, for example, may convert into three different forms:
2-hydroxyestrone protective and active
4-hydroxyestrone carcinogen and active
16-alpha-hydroxyestrone carcinogen and active
Scientists have identified 2-hydroxyestrone as a “good estrogen,” while 16-alpha-hydroxyestrone and 4-hydroxyestrone (“bad” estrogens) have been associated with the development of certain types of cancer, like breast and ovarian with uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts and fibrocystic breasts.
In 2002, the Women’s Health Initiative study of postmenopausal women with an average age of 65 and older found that taking combination HRT increased the risk of breast cancer, heart disease, stroke and blood clots. The study found that the women using synthetic estrogen in combination with progestin (a product called PremPro), versus women who were on a placebo, had a 26% increased risk of developing breast cancer, 41% increased risk of strokes, a 200% increased risk of blood clots, and a 29% increased risk of heart attacks or heart disease. Another part of the WHI found that women on PremPro instead of experiencing cognitive improvement, which technically they should have given the role of estrogen and progesterone in brain functions, had double the risk of developing dementia in the 65 and up age group.
As men age their SHBG starts to increase leading to a decrease in free testosterone and estrogen levels also start to increase. This is partly because aging men in some cases convert more of their testosterone into estradiol, by means of the enzyme aromatase.6 Of the remaining testosterone, much of it is bound to sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG). As long as free testosterone is low and the relative estrogen (estradiol and estrone) is high, a man will store fat around their belly, hence the “pot belly”.7 Low plasma levels of SHBG and free testosterone have been linked with increased insulin resistance and risk for type 2 diabetes in males.
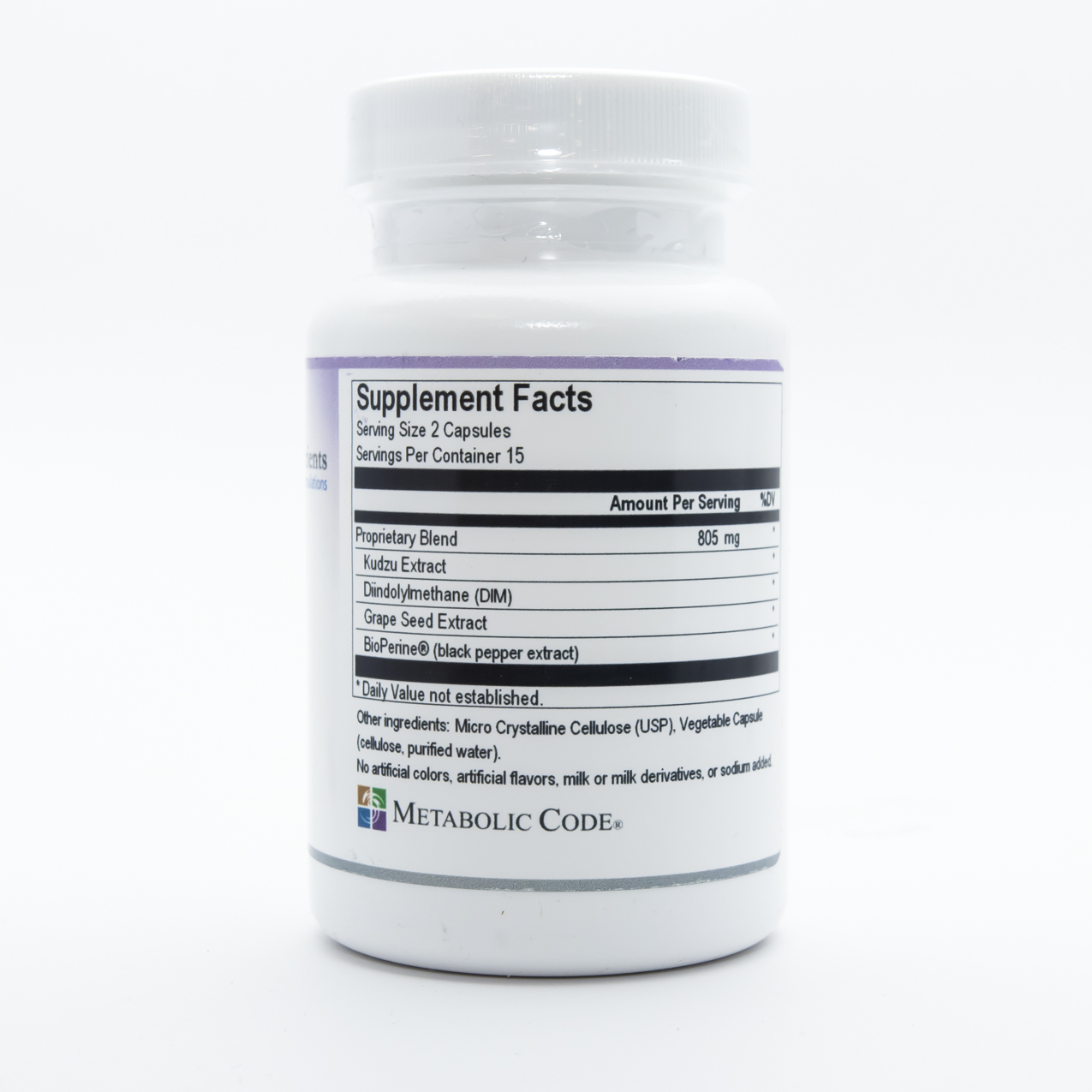
EstroMetab contains the herbal supplement Kudzu root (Pueraria lobata), which contains isoflavones that are reported to bind to estrogen receptors in laboratory studies. It also contains diindolylmethane (DIM), extracted from cruciferous vegetables and reported to help improve estrogen conversion to the friendlier 2-OH estrone form.. EstroMetab also contains the patented extract of black pepper, BioPerine®, which is reported to help improve absorption and bioavailability of dietary supplements.
Ingredients
- Kudzu root
- Diindolylmethane
- Grape seed extract
- BioPerine
Processing...